How to Buy Bitcoin on Cash App: Step-By-Step Guide 2024
March 29, 2022What are Sundry Expenses?
May 23, 2022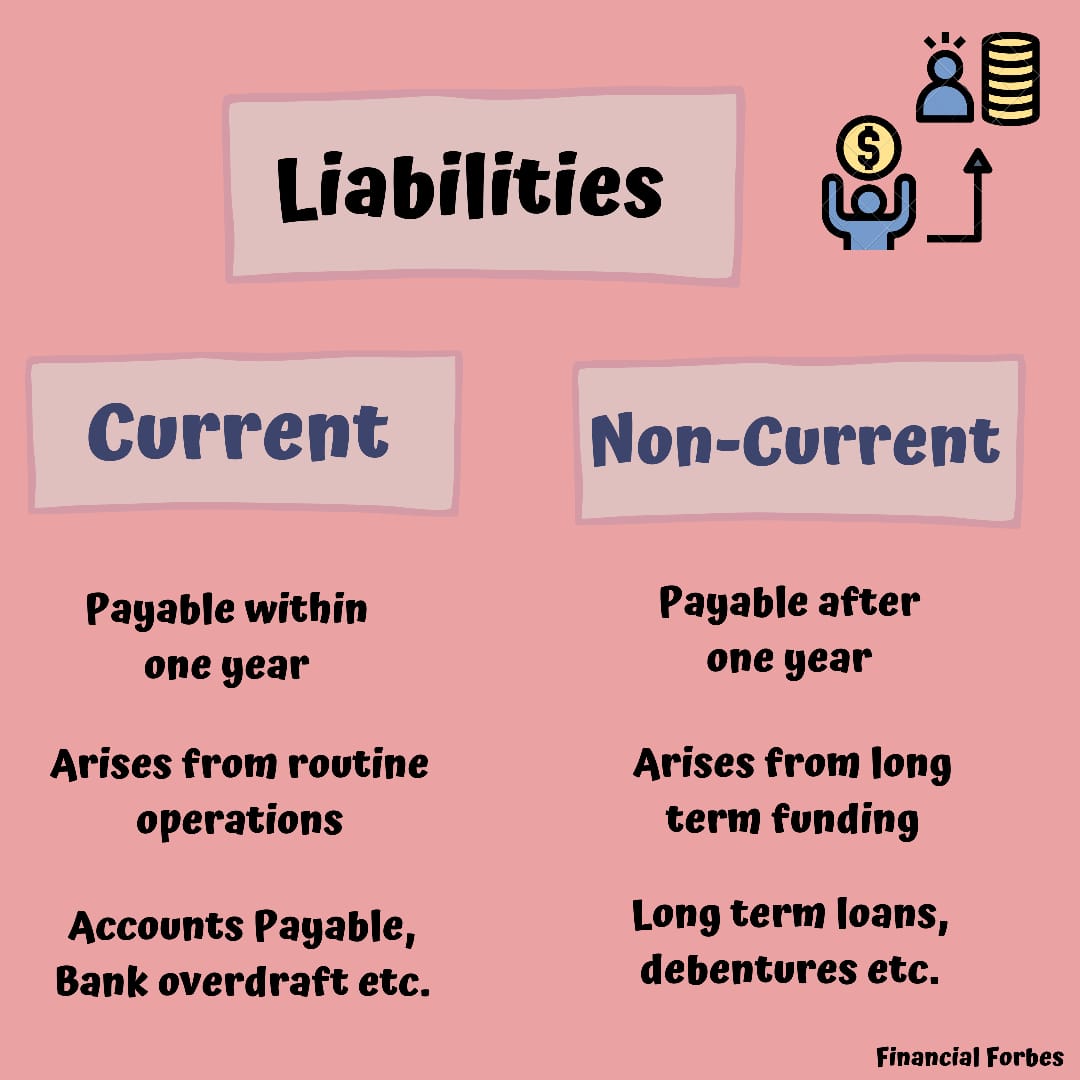
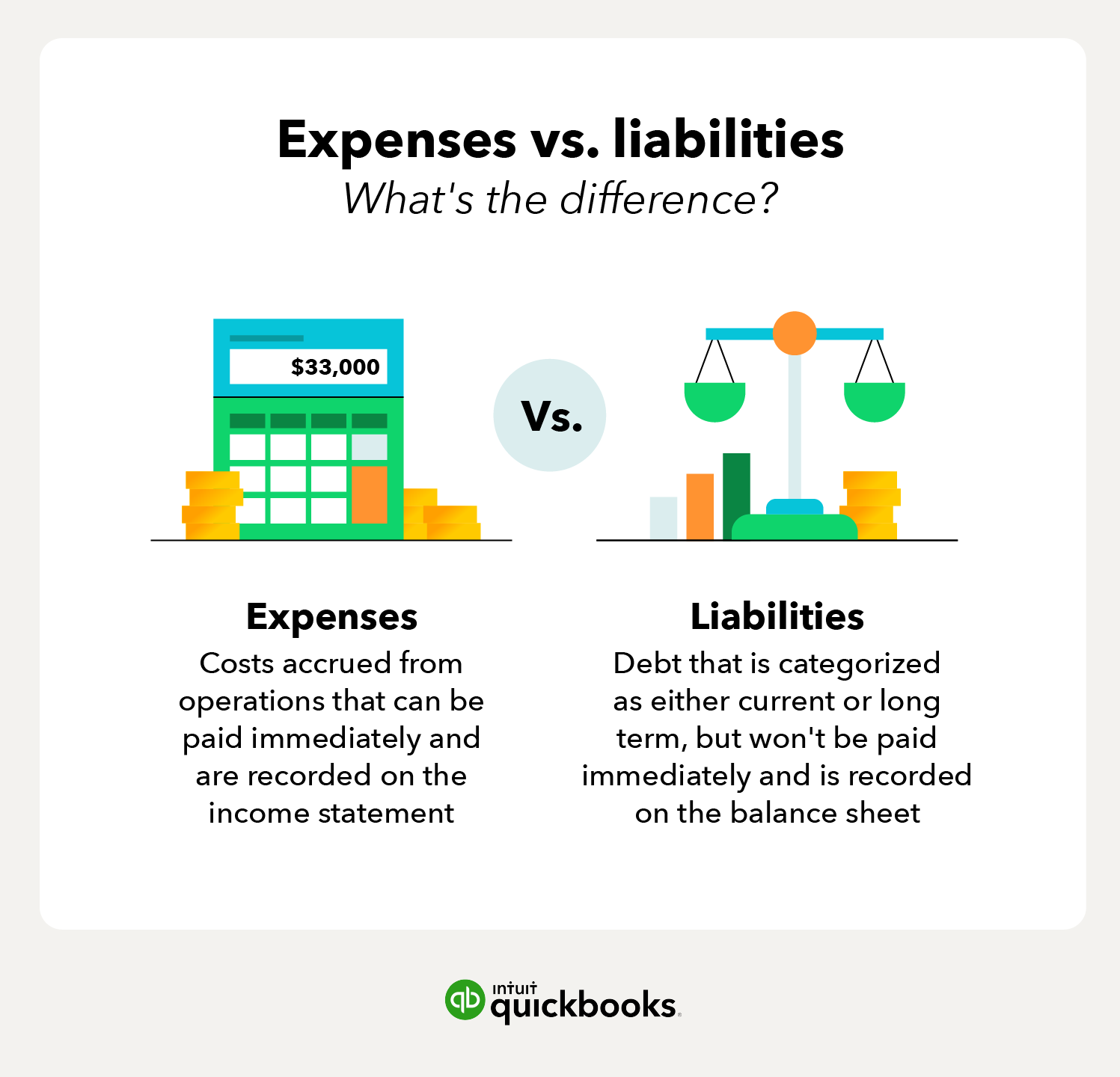
Generally, liability refers to the state of being responsible for something, and this term can refer to any money or service owed to another party. Tax liability, for example, can refer to the property taxes that a homeowner owes to the municipal government or the income tax he owes to the federal government. Once liabilities are paid, they become expenses and are no longer included on a balance sheet. According to the accounting equation, the total amount of the liabilities must be equal to the difference between the total amount of the assets and the total amount of the equity.
Accounts Payable
He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. This article aims to expand your knowledge about the definition, type of liabilities, and various examples of liabilities. Sign up to receive more well-researched small business articles and topics in your inbox, personalized for you. Our article about accounting basics discusses in detail the concepts you need to understand small business accounting.
Liabilities in Accounting
In case of sudden requirements, a liability helps entities pay for operations and then return the finance as applicable to the lenders. Less liquidity is required to pay for long-term liabilities as these obligations are due over a longer timeframe. Investors and analysts generally expect them to be settled with assets derived from future earnings or financing transactions. Short-term debt is typically the total of debt payments owed within the next year. The amount of short-term debt as compared to long-term debt is important when analyzing a company’s financial health.
SG&A Meaning: Selling, General & Administrative Expenses (Definition)
Long-term liabilities cover any debts with a lifespan longer than one year. Examples would be mortgages, rent on property, pension obligations, auto loans, and any other large expense that is paid over the course of multiple years. Whatever entails current debts or financial burden is a liability.
How Current Liabilities Work
- Examples of liabilities include deferred taxes, credit card debt, and accounts payable.
- They’re recorded on the right side of the balance sheet and include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues, bonds, warranties, and accrued expenses.
- A liability is anything you owe to another individual or an entity such as a lender or tax authority.
- Our method aligns with standard financial practices to provide accurate calculations.
- A) They represent ownership in the company.B) They typically require periodic interest payments.C) They have no maturity date.D) They are considered short-term liabilities.
When a company issues a bond, it is essentially borrowing funds that it must repay with interest over a specified period. Bonds come in various forms, with different structures and risk levels, tailored to meet the financing needs of the company and the investment preferences of bondholders. Debt is generally cheaper than equity due to the tax benefits of interest payments and because debt holders take lower risks as they have priority in case of liquidation. However, excessive debt can increase the cost of capital by raising the risk of financial distress. Debt financing involves borrowing funds, which the company must repay over time with interest.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
Liabilities refer to things that you owe or have borrowed; assets are things that you own or are owed. The value of shares and ETFs bought through a share dealing account can fall as well as rise, which could mean getting back less than you originally put in. In finance, the equity definition is the amount of money the owner of an asset would have… Liabilities are used by investors to estimate and compare companies’ performance. This is not always straightforward as the way liabilities are recorded can vary. AP typically carries the largest balances, as they encompass the day-to-day operations. AP can include services, raw materials, office supplies, or any other categories of products and services where no promissory note is issued.
This is why it’s critical to understand the differences between current and long-term liabilities. Plus, making sure that they get recorded properly on your balance sheet is just as important. Conversely, companies might use accounts payables as a way liabilities examples to boost their cash. Companies might try to lengthen the terms or the time required to pay off the payables to their suppliers as a way to boost their cash flow in the short term. The portion of the vehicle that you’ve already paid for is an asset.
An asset is anything a company owns of financial value, such as revenue (which is recorded under accounts receivable). Some loans are acquired to purchase new assets, like tools or vehicles that help a small business operate and grow. No one likes debt, but it’s an unavoidable part of running a small business.
Understanding what liabilities are in accounting, as well as the most common examples of each type, can help you track and identify them in your balance sheet. US GAAP requires some businesses to disclose or report contingent liabilities. Small businesses that aren’t required to comply with the US GAAP may opt not to consider contingencies in financial reporting.
